 Read time: 3 Minutes
Read time: 3 Minutes
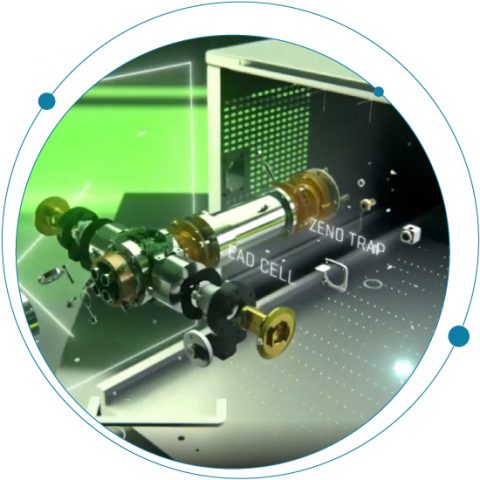
A powerful combination: The Zeno trap and electron activated dissociation (EAD) fragmentation Sensitivity is a fundamental performance characteristic of a mass spectrometer. Increasingly higher sensitivities are in constant demand in order to characterize and quantify analytes that are at an ever decreasing abundance.
Electron activated dissociation or EAD is a ground-breaking approach for tandem mass spectrometry applications. While the industry standard collision induced dissociation (CID) has proven to be an invaluable tool for MS/MS experiments, the data produced using CID can leave gaps.
Together the Zeno trap and EAD fragmentation are a powerful combination.
You can now discover new levels of control, with a step change in fragmentation technology. You have the ability to create reproducible fragmentation patterns through high-energy collisions (CID) or, precisely disassemble molecules, exploring new perspectives. You will be able to fine tune fragmentation energies, allowing controlled electron-activated dissociation of all molecule types.
These advanced fragmentation mechanisms create a myriad of insight within your reach. Zeno trap pulsing unlocks extraordinary sensitivity gains, uncovering information that has always existed undetected, adding new perspective to your quantitative and qualitative data.
Together the Zeno trap and EAD provide the ability to acquire key MS/MS features needed to:
- Characterize large molecules including post-translational modifications
- Elucidate positional isomers on small molecules and lipids
- Identify and quantify proteins and peptides at unparalleled speed
The Zeno trap: The next era of sensitivity for accurate mass
Ions are accumulated in the Zeno trap before being pulsed rapidly into the TOF, meaning up to 20x more ions can be detected. Consequently, each TOF experiment contains more useful MS/MS information, particularly on lower abundance species that were previously undetectable, introducing our customers to a new level of sensitivity.
Electron activated dissociation (EAD): A step change in fragmentation technology The ability to tune electron kinetic energy extends the utility of the approach to all molecule types from singly charged small molecules to large multiply charged proteins. EAD allows for a range of reagent free electron-based fragmentation mechanisms within one device, and has the capability to fragment peptides whilst retaining critical MS/MS information for both identification and localization of PTMs. Unlike other electron based fragmentation techniques, EAD delivers reproducible, consistent data, even at fast scan speeds, compatible with UHPLC timeframes, delivering higher efficiency than ETD.
A revolution in accurate mass has arrived. The ZenoTOF 7600 high-resolution accurate mass system combines the power of Zeno trap pulsing with EAD fragmentation which allows for detection of very low abundant diagnostic fragment ion species leading to greater sequence coverage.
Now, you can watch as rare data becomes your everyday and your toughest challenges become your greatest advantage. Now, new discovery is not only possible, but quantifiable.
Welcome to the Zeno revolution.
Related to: RUO-MKT-19-13372-A, RUO-MKT-19-13373-A, RUO-MKT-18-13402-A and RUO-MKT-17-13406-A
Image based on this:






 Contact Support
Contact Support
0 Comments