 I recently had the opportunity to catch up with Baljit Ubhi to discuss the top questions you’re asking in regards to using Microflow HILIIC Chromatography for Targeted Metabolomics. Here’s what Bal said:
I recently had the opportunity to catch up with Baljit Ubhi to discuss the top questions you’re asking in regards to using Microflow HILIIC Chromatography for Targeted Metabolomics. Here’s what Bal said:
Why is analyzing polar metabolites so challenging?
Many of the metabolites of interest in the study of metabolomics are extremely polar and therefore often unable to be analyzed through traditional coupling of reversed phase (RP) chromatography and mass spectrometry. Also to detect and quantify key metabolites from pathways of biochemical importance, samples must be run on both reversed phase and normal phase, in negative and positive ion modes requiring a total of four injections.
How does this workflow address those challenges?
We have implemented hydrophilic chromatography (HILIC) with microflow and mass spectrometry to develop a method for screening over 300 polar metabolites. HILIC allows separation by partitioning of analytes between an aqueous enriched layer of a polar stationary phase. HILIC conditions typically use high organic, with a moderate amount of a salt (i.e. 20-100mM ammonium formate or acetate, pH 4.4 or 5.5. respectively). This method deviates by having 20 mM ammonium hydroxide in both mobile phases to provide constant pH of 9.0 during the chromatographic separation. The high pH deprotonates the stationary phase and allows for better selectivity of the polar metabolites. The method is multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) with positive/negative polarity switching allowing the collection of these key metabolites in a single injection!
What is unique about the sample prep and chromatography?
While microflow has become increasingly popular for many applications, microflow for metabolomics has not been readily employed because the typically used (aqueous) sample solvent does not allow for injecting larger volumes of samples without sacrificing chromatographic resolution. However, by simply reconstituting the sample in an organic solvent (95% acetonitrile, pH 9), we were able to inject up to 5 µL onto the microLC column, while maintaining excellent peak shape.
How does microflow LC compare to traditional high flow LC approaches for metabolomics? What makes it better?
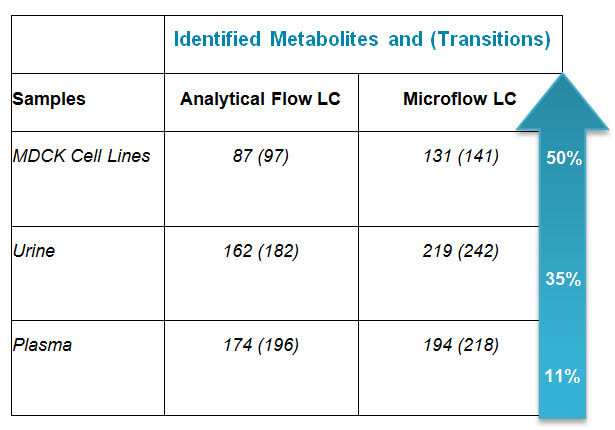
The microflow Luna-NH2 HILIC chromatography provides excellent chromatographic separation of polar, hydrophilic metabolites. The cross-linked aminopropyl phase gives a slightly different selectivity than the traditional amide phase; it gives higher coverage of the metabolome when compared to the amide functionality. This allows for improved sensitivity with signal-to-noise (S/N) improvement of up to 60X and up to 50% higher coverage of the metabolome than traditional analytical approaches (see table above).






 Contact Support
Contact Support
0 Comments