Q&A with Sean McCarthy Global Market Manager, Biologics, SCIEX MAM is an acronym for Multiple Attribute Method. In short, MAM is a method which may be applied for characterization of a biotherapeutic to understand its sequence, identify liabilities, identify...
Tags

Celebrating customer experience: Insights from SCIEX leaders
Introduction Customer Experience Day (CX Day) is a special occasion for SCIEX, celebrated every first Tuesday in October. It’s a day dedicated to recognizing the incredible value of our customers and the relentless dedication of our associates who strive to make...

LC-MS system replacement: Are you ready?
Meeting deadlines in a bioanalysis laboratory can be a big challenge. Older, less sensitive and less reliable LC-MS systems make it even more difficult. Even the disruption caused by the installation and validation can be disconcerting and delay decisions. Does this sound familiar?
Questions and answers to help improve your mycotoxin analysis
During a recent webinar I shared method details for mycotoxin analysis on the SCIEX 7500 system. In this blog i will share the Q&A for the submitted questions that we did not have chance to answer during the live webinar.
Optimized rolling collision energy curves for IDA and SWATH DIA for peptides
During data dependent acquisition (DDA or IDA) or SWATH acquisition, the collision energy can be automatically adjusted according to the mass/charge and charge of the peptide. This dependency has been well characterized on our QTOF systems. By selecting rolling...

Back to the new basics: Part 1 | Making the leap from GC-MS to LC-MS
Producing accurate results quickly in a demanding environment is no easy feat for analytical scientists. What’s more, many of us are constantly questioning ourselves—I certainly am—about whether we are employing the best technique for the analysis at hand.
It’s an overwhelming thought, considering the wide range of tools that are available to choose from, each of which offers varying levels of capacity, sensitivity, selectivity, specificity and cost. How do you meet the unique needs of your organization without breaking the bank? I get it, and I’m not here to convince you it’s easy. My aim is to guide you through the process to help you make the right decision for you.
MRM method transfer from a SCIEX Triple Quad or QTRAP 6500+ system to the SCIEX 7500 system
General recommendations when beginning method development Objective: The purpose of this document is to provide a quick reference for transferring MRM-based quantification methods from a SCIEX Triple Quad or QTRAP 6500+ system to a SCIEX 7500 system. While the best...
Adapting a SCIEX high flow source for microflow LC
To set up a SCIEX high flow source for microflow LC (Turbo V ion source, DuoSpray source or IonDrive Turbo V ion source), first you must replace the wider bore electrodes with more narrow bore hybrid electrodes. Note with the OptiFlow Turbo V ion sources, there are...

Identifying the unknown PFAS profile in firefighting foams/AFFF
According to a recent study from Harvard University, the US EPA, and NIEHS, traditional targeted analysis techniques poorly characterize the PFAS composition of contemporary PFAS-based firefighting foams, know as aqueous film-forming foams (AFFF). Using the EPA 533 PFAS drinking water method for the analyte list, the researchers found that targeted mass spectrometry methods accounted for <1% of organic fluorine content. This is important because it demonstrates that targeted analysis methods miss nearly all the PFAS compounds in modern AFFF mixtures, thus underestimating the risk to human health and the environment.
sMRM Concurrency Calculator
This excel sheet allows you to quickly estimate the MRM concurrency and approximate dwell time for your Scheduled MRM Algorithm acquisition method. Paste your MRM method with retention times into the input tab then calculate the Excel workbook. Plots will update to...

The risky business of aflatoxins in milk
If you’re in the dairy or food testing business, you know the threat aflatoxins pose. Aflatoxins are a type of mycotoxin produced by Aspergillus parasiticus, aspergillus flavus , and rarely aspergillus nomius.1 These are likely the most extensively researched group of mycotoxins because of their adverse health effects.2 What’s more, they are widely found in a variety of crops, namely maize, tree nuts, and spices. Believed to be primarily caused by rising temperatures and humidity, these naturally occurring fungi grow on crops in the field, or during storage of feed and raw materials, where they can potentially produce toxins that enter the food chain.

The Not So Hidden Truth about Climate Change How It’s Poisoning Your Food
Did you know climate change could be poisoning your food? According to the United Nations Environmental Program (UNEP) report on Emerging Issues of Environmental Concern, rising temperatures are making crops more toxic.

Guardians of Antibiotics
This second is a blog series on the global war: Rise of Superbugs! Part 1 took a critical look at the antibiotic threat we face in today’s battlefield. The waning effectiveness of antibiotics as we head into what may seem like a post-antibiotic era has impelled new reformation to at the very least control antibiotic usage to ensure food safety.

Protein Quantitation Workflows using the TripleTOF 6600: A Case Study for Rituximab
Although the triple-stage quadrupole (QQQ) mass spectrometer remains the pillar for quantitative LC-MS/MS bioanalytical assays, due in part to the platforms’ high duty cycle when operated in multiple-reaction monitoring (MRM) mode, the applicability of high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) has become of increasing importance for protein quantitation given the complexity of proteolytically digested samples in the surrogate peptide approach. While the QQQ demonstrates high sensitivity and specificity, the relatively low-resolution measurement of m/z may fail to differentiate analyte response from nominally isobaric background interference. In contrast, HRMS with accurate mass assignment of product ion allows interference to be resolved through judicious selection of a post-acquisition mass extraction window whose tolerance is largely dictated by the effective resolution and stability of mass calibration.

Rise of the Super Bugs
The term “antibiotic-free” is becoming more and more popular in food advertising these days. Take Subway for example; in March the company elevated their antibiotic-free policy and introduced a new antibiotic-free rotisserie-style chicken sub, and they plan to, “Nix antibiotics in all its meat by 2025.”

Glyphosate, a Polar Pest Put to Test
No other pesticide has courted more media attention and controversy in recent months than glyphosate, with governments and national agencies debating its use and health effects.

Using Mass Spec to Detect Trace Explosives
The importance of protecting a country’s border is a very topical issue. The war on drugs and terror is a 24/7 task 366 days a year (2016 is a leap year). The government agencies in charge must be vigilant and maintain instrumentation to prevent terrorism, drug trafficking, and other illegal activities. Mass Spectrometry is rapidly becoming the instrument of choice for border agencies throughout the world when it comes to explosive trace detection and forensic drug compounds.

Routine Food Testing Using Mass Spectrometry
These days, it is not uncommon to hear about the overzealous application of pesticides to crops or the injection of antibiotics into animals. From grocery stores to restaurants, our food is at risk. How then, can consumers be assured that chemical contaminants like these , not to mention the risk of mycotoxin compounds are not making their way to your dinner table?

Quantify and Identify Pesticides in Complex Food Samples Using the QTRAP 6500 LC-MS/MS System
Recent regulations on food analysis require screening for pesticides using confirmatory techniques, such as GC-MS and LC-MS/MS. More than 1000 pesticides are used worldwide and, along with their metabolites and degradation products, are present in food. There is a demand for powerful and rapid analytical methods that can identify pesticides with high confidence in a broad range of food matrices and quantify at low concentrations with good accuracy and reproducibility. Challenges for pesticide residue laboratories at the moment are the request to test for more compounds, in a wider range of samples, all without sacrificing data quality.

Fast, Efficient, Disulfide Bond Mapping Using BioPharmaView™ Software
Fast LC-MS acquisition and automated data processing will help you speed up peptide mapping of your biotherapeutic, including critical disulfide bond and post-translational modification characterization. SCIEX helps you untangle the complexity of disulfide bonds, speeding up your characterization process.
Bottom-Up Proteomics: A Discussion with Christie Hunter
Biocompare recently featured an article on Bottom-Up Proteomics. I had a chance to follow up with Christie Hunter and expand on some of the questions featured in the article:

Characterize and Monitor Host Cell Proteins (HCPs) Using SWATH Acquisition Technology
During drug development, the removal of impurities and purification of a final drug product is absolutely essential in order to ensure the safety and efficacy of a therapeutic drug. Of particular concern for biologics are impurities that can stem from host cell proteins. Because biologics are developed through cell culture and fermentation within a host cell, proteins from this host cell can be co-purified with the final biologic. These host cell proteins or HCPs can cause the final product to have undesired side-effects such as eliciting an immune response in patients taking the drug, or affecting the drug’s stability or efficacy. As a result, regulating agencies require drug companies to monitor levels of HCPs during the development and purification of a biologic and to remove HCPs to an acceptable level in the final biotherapeutic product.
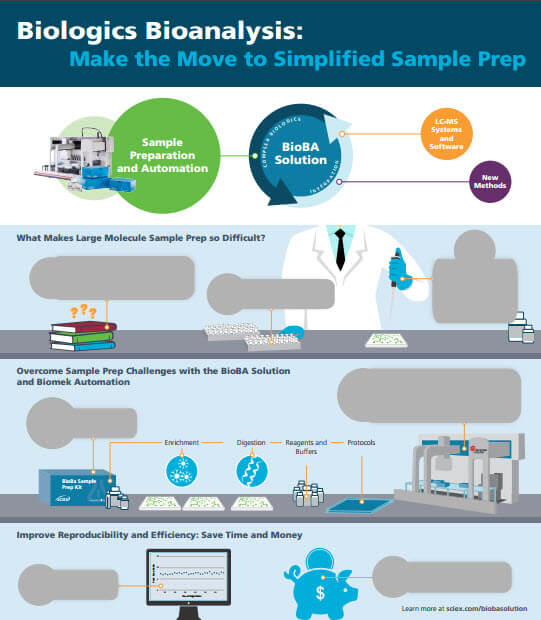
Simplifying Biologics Bioanalysis Sample Prep
These days, everyone seems to be furiously scratching tickets to become instant winners, but I’ll bet you didn’t expect to find sample prep tips that way. For large molecule bioanalysis, preparing your samples can be one of the biggest challenges. It’s a whole different world from traditional small molecule bioanalysis. SCIEX has developed techniques and automation that make biologics sample prep simpler and faster, with reproducible results.

The Connection Between Mass Spectrometry and Space Exploration
Mass spectrometry has been used for some pretty fascinating applications in our world – like testing for steroid use in athletes1, measuring pesticides in grapes2, assessing the efficiency of a psoriasis drug3, and whether that expensive bottle of 100% olive oil is, well, really 100% olive oil.4 But did you know mass spec is also used out of this world? Like… in space?
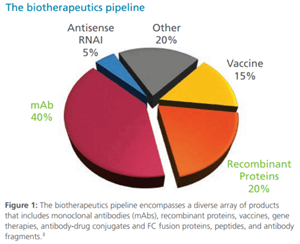
The Future of Biologics Drug Development is Today
Since the 1982 approval of Eli Lilly’s recombinant human insulin, Humulin, biotherapeutic drug development has steadily grown into a global market valued at $140 billion in 2013, increased from $25 billion in 2001
A Hybrid LBA/LC-MS Assay – Your Questions Answered
Last week we posted a blog on Biologics Bioanalysis Key Challenges, where we presented a webinar on those key challenges.
Using Mass Spectrometry to Identify and Quantify Contaminants in Water Samples
Access to clean wholesome water is one of our basic human rights. Human engineering has designed incredible methods to collect, filter, purify, store and distribute water to billions of us worldwide, but does this mean that our water is completely safe to drink? Also,...

LC-MS/MS Method for Biotherapeutic Drug Development Challenges
Traditionally, the pharmacokinetic profile of biotherapeutics such as insulin glargine, adalimumab, trastuzumab and others, used gold standard LBAs to assess dose-response during drug discovery and development. However, LBAs require a specific antibody reagent to be developed for each mAb variant, a process that is often incompatible with the compressed timeframes encountered during the initial stages of drug development.

QTOF Technology for Targeted and Unknown Forensic Drugs Screening Workflows
In this study, the Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene (WSLH) outlines the comparison of their existing technology and how SCIEX LC-MS/MS systems can assist them in their forensic research. The WSLH routinely analyze for 300 forensic drug compounds in over 18,000 samples per year.

Expert Advice to Help You with Routine Food Testing in the Lab
Between 3-6 November 2015, the Recent Advances in Food Analysis (RAFA) 2015 Symposium took place in Prague, Czech Republic.
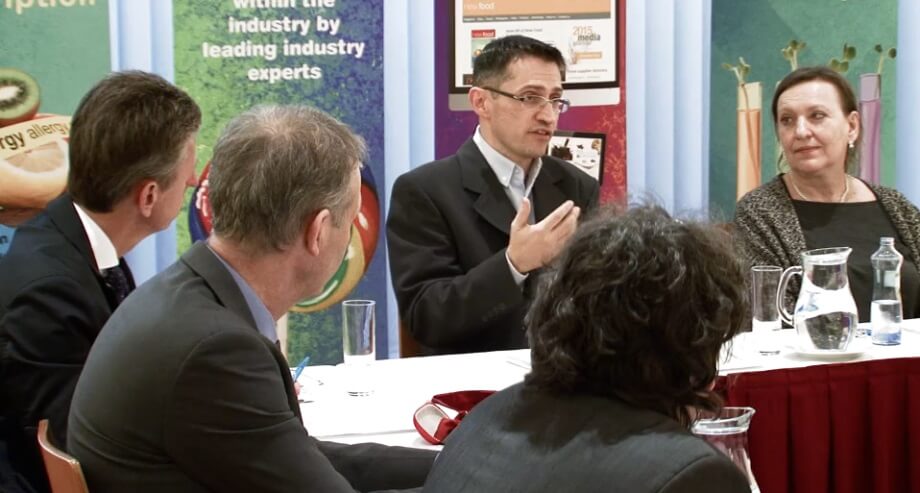

Contaminants and Novel Approaches in Food Analysis
During RAFA 2015, New Food Magazine hosted a roundtable (sponsored by SCIEX) to bring together experts with routine food testing backgrounds to discuss the latest industry trends, challenges, recent technological advances, and expectations of future laboratories.